Exploring the potential health benefits of lion’s mane mushroom, particularly in relation to depression, has piqued the interest of both researchers and individuals looking for natural remedies. Lion’s mane, a unique mushroom recognized for its nerve-regenerative properties, is being studied for its potential to improve mental health. While traditional medicine has primarily relied on pharmaceutical interventions, the shift towards natural supplements has led to increased attention on the therapeutic effects of lion’s mane on depression symptoms.
Determining the optimal lion’s mane dosage for depression is crucial. The right amount can influence the efficacy of the treatment and the overall outcome. Recent studies suggest that medium to high doses of lion’s mane extract can have a positive impact on depressive behavior, offering hope for a natural approach to managing mental health. As with any supplement, it is essential to consider individual differences and consult with healthcare providers to establish a safe and effective dosage tailored to your needs.
The promising results from preliminary research on lion’s mane supplementation underscore the importance of further investigation into its use as a dietary intervention for depression. While the mushroom’s potential is undeniable, understanding the correlation between the dosage and its health benefits will be paramount in its application as a supportive treatment for depression. As interest grows and more data become available, the integration of lion’s mane as a component of mental health management could offer a complementary approach to traditional treatments.
Understanding Lion’s Mane
Table of Contents
In your exploration of Lion’s Mane, you’ll uncover the specifics of its taxonomy and historical significance as a medicinal mushroom.
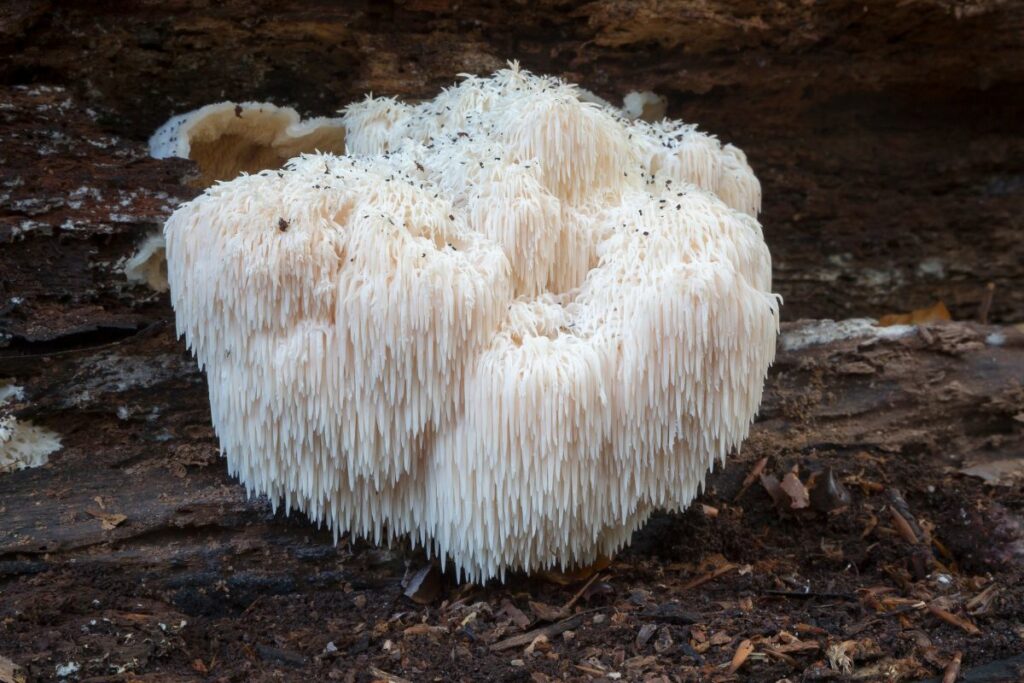

Taxonomy and Description
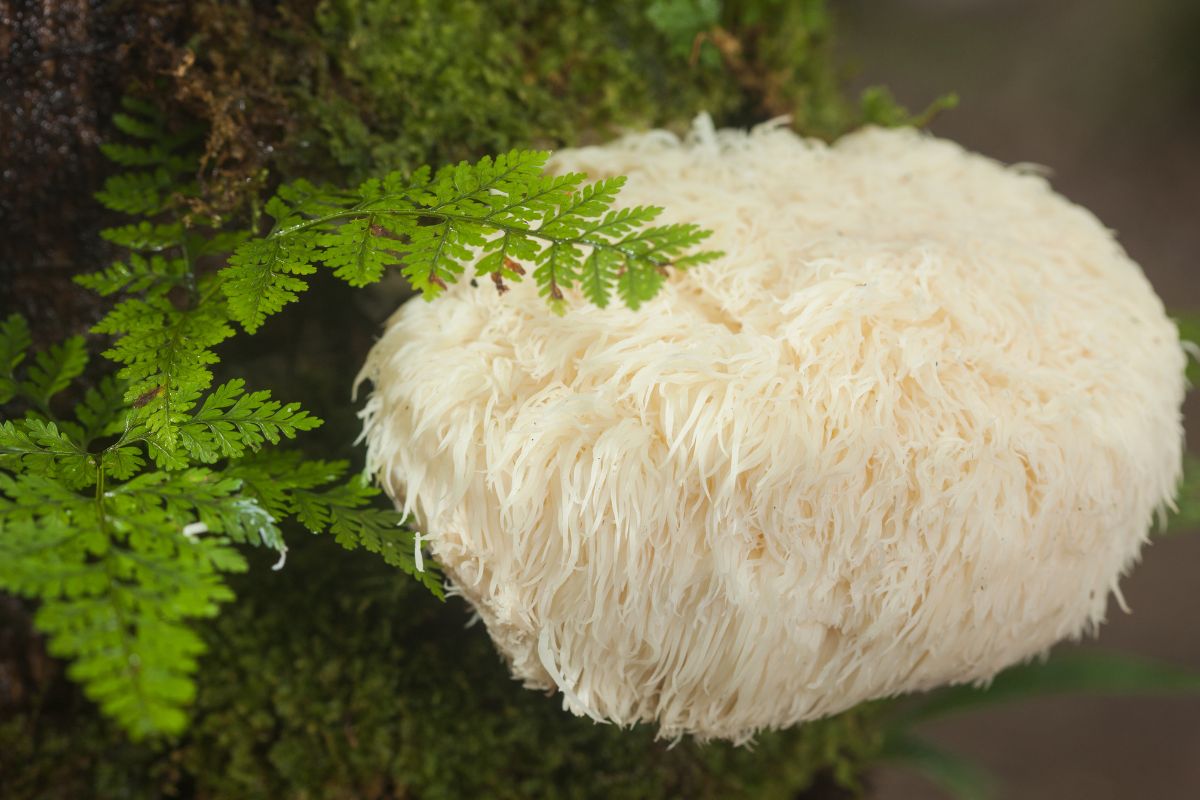
Hericium erinaceus, more commonly known as Lion’s Mane mushroom, belongs to the fungus kingdom and is categorized within the Hericium genus. It is an edible and medicinal mushroom, often recognized for its distinctive white, spiny projections that resemble a lion’s mane. This unique fungus thrives on both living and dead hardwood trees and is found in North America, Europe, and Asia, where it is also known by the name Yamabushitake.
Historical Uses and Cultural Significance
Lion’s Mane has a storied past, revered for its medicinal properties in traditional Chinese medicine. Historically, it has been consumed for its potential cognitive and neurological benefits, and it continues to be a subject of interest in contemporary research, particularly for its potential effects on mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. The mushroom has woven itself into the cultural fabric of various Eastern societies, where it’s not only used for health but also appreciated as a gourmet culinary ingredient due to its rich, seafood-like flavor.
Lion’s Mane and Depression
Lion’s Mane mushroom has gained attention for its potential in managing depression, a prevalent mental health condition. This complex natural substance is thought to interact with key neurotransmitters that influence mood and cognitive function.
| Aspect | Information |
|---|---|
| Active Compounds | Hericenones and erinacines, compounds found in Lion’s Mane, may have neuroprotective and neuroregenerative effects. These compounds may stimulate nerve growth factor (NGF) production. |
| Potential Benefits | – Neuroprotection and support for nerve growth |
| – May have anti-inflammatory properties | |
| – Early research suggests positive effects on mood and cognitive function | |
| Research Status | Limited human studies; more research needed |
| Caution | Individuals with allergies to mushrooms should avoid Lion’s Mane. If considering Lion’s Mane for mental health, consult a healthcare professional. |
Evidence of Antidepressant Effects
Studies on animals suggest that extracts from Lion’s Mane mushroom could improve depressive behavior and potentially act as an antidepressant. For instance, a dietary supplement derived from chlorella and Lion’s Mane mushroom was found to alleviate depression in aged mice. While these findings are promising, it is crucial to acknowledge that human trials are needed to confirm efficacy.
- Animal Research: Medium and high doses of chlorella and Lion’s Mane extract have improved depressive behavior in aged SAMP8 mice.
How Lion’s Mane Affects Neurotransmitters
Lion’s Mane mushroom may benefit your mental health by influencing neurotransmitter levels such as serotonin and dopamine, which are often imbalanced in those suffering from mood disorders and major depressive disorder. The mushroom contains compounds that can stimulate nerve growth factor (NGF) synthesis, possibly leading to improved brain function and mood regulation.
- Neurotransmitter influence: Lion’s Mane supplementation has been associated with lowered depression and anxiety scores in young adults.
Your understanding of Lion’s Mane’s impact on mental well-being could be fundamental in exploring alternative treatments for mood disorders including depression.
Working Mechanism
When considering Lion’s Mane mushroom for depression, it’s essential to understand how it affects your brain’s functioning. Two key components, hericenones and erinacines, play critical roles in stimulating neurogenesis and Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) production.
Role of Hericenones and Erinacines
Hericenones and erinacines are bioactive compounds found exclusively in the Lion’s Mane mushroom. These compounds are powerful because they have the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. Once in your central nervous system, they can stimulate the production of nerve growth factor (NGF). NGF is vital for the growth, maintenance, and survival of neurons, which are the nerve cells responsible for sending and receiving signals in the brain.
Neurogenesis and Nerve Growth Factor
Neurogenesis, the process of forming new neurons, occurs in your brain’s hippocampus—a region that’s critical for memory and learning. Lion’s Mane mushroom aids in this process by enhancing the expression of NGF. Increased levels of NGF can lead to the development and strengthening of neurons, potentially improving cognitive function and contributing to better mental health.
Through these mechanisms, Lion’s Mane mushroom has the potential to support your mental agility and may alleviate symptoms of depression by fostering a more resilient and plastic central nervous system.
Remember, while the mechanisms of action are backed by scientific research, individual responses to Lion’s Mane supplementation can vary. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Effective Dosage
Determining the proper dosage of Lion’s Mane mushroom for addressing symptoms of depression is crucial for its potential effectiveness. Your unique needs and the form of the supplement may impact the amount you take.

Dosage Guide and Recommendations
As you seek to incorporate Lion’s Mane into your regimen for depression, it’s essential to start with the recommended dosage found on product labels, which can vary depending on the manufacturer and form of the supplement you choose. For capsules, a common dosage ranges between 500 mg to 3,000 mg taken daily. If you’re opting for a powder form, a typical serving might be one to two teaspoons, which can be mixed into a beverage or meal. It’s often suggested to start with a lower dosage to see how your body reacts and gradually increase if necessary, without exceeding the manufacturer’s maximum recommendations.
Variations by Product Form
Each form of Lion’s Mane, such as capsules, powders, extracts, and teas, will have its own dosage guidelines.
- Capsules: Generally convenient, they offer a precise dosage and can range from 500mg to upwards of 1,000mg per capsule.
- Powder: This versatile form can be easily added to various dishes and typically comes with a scoop for measurement. Adjust the amount according to your taste and the concentration of the powder.
- Extract: Liquid extracts and tinctures can be potent, and the dosage is often measured in droplets or milliliters. Because of their concentration, the required dose may be smaller, usually a few drops to a couple of milliliters per day.
- Tea: Brewing Lion’s Mane as a tea involves steeping the dried mushroom or tea bag in hot water. The strength of tea can vary, so follow the package instructions for the recommended amount.
Each product should provide specific instructions, and it’s essential you adhere to these while considering any personal health factors. If you’re unsure about the right dosage for your situation, consulting with a healthcare provider is advisable.
Remember, the objective with any supplement, including Lion’s Mane, is to find the smallest effective dose that provides the desired benefits. Since Lion’s Mane dosage for depression hasn’t been universally established, individual experimentation under professional guidance is key.
Safety and Side Effects
When considering Lion’s mane mushrooms for depression, it’s crucial to understand the safety profile and be aware of possible side effects. Personal response to supplements can vary, and while Lion’s mane is largely considered safe, some individuals might experience adverse reactions or interactions with medications.
Common Adverse Reactions
Most people tolerate Lion’s mane well, however, side effects can occur. These often include:
- Gastrointestinal discomfort
- Itchiness or skin rash, which might be linked to mushroom allergies
It’s wise to start with a low dosage and gradually increase to see how your body responds.
Potential Interactions with Medications
Lion’s mane mushrooms might interact with certain drugs, particularly:
- Blood thinners: Compounds in Lion’s mane may have blood-thinning effects, which could amplify the action of anticoagulant medications.
- Immunomodulating drugs: Since Lion’s mane can modulate immune system function, it may interfere with these types of medications.
Always consult with a healthcare provider to ensure that Lion’s mane supplements do not interfere with your current medications or medical conditions.
Additional Health Benefits
While Lion’s Mane mushroom is discussed in the context of depression, it extends far beyond that, impacting your cognitive function, immune response, and potentially even affecting aging. Explore how this remarkable fungus might contribute to your overall health.

Cognitive and Neurological Health
Your brain’s health is paramount, and Lion’s Mane shows promising effects in supporting cognitive function and possibly reducing the risk of neurological diseases. Studies suggest that Lion’s Mane can stimulate the production of Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) which is crucial for the maintenance and growth of neurons. Consistent use has been linked to a reduction in cognitive impairment, and it may provide benefits to those dealing with mild cognitive impairment and possibly even Alzheimer’s disease.
Immune System and Inflammation
Your immune system’s strength is vital for your overall wellness. Lion’s Mane exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, which are integral to the immune response. By potentially lowering inflammation, it might assist your body in fighting off infections and diseases more efficiently. This fungus has been studied for its role in enhancing the immune function, which could be an added advantage for your long-term health.
Potential Benefits for Aging and Longevity
Aging is a natural process, but the rate and manner in which it happens can vary. Lion’s Mane offers a compelling profile for those interested in longevity. Some research implies that its antioxidant properties can counteract the decline in cognitive function associated with aging and even offer some defense against neurodegenerative conditions like dementia. By potentially slowing age-related cognitive decline, Lion’s Mane might support a longer span of mental acuity.
In your journey to maintain and improve mental health and overall wellness, understanding and utilizing the potential health benefits of supplements like Lion’s Mane could be a beneficial part of your regimen.
Nutritional Profile and Consumption
In considering Lion’s Mane mushroom as a dietary supplement for depression, you should understand its nutritional composition and how it can vary when consumed raw versus cooked.
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | ~22 |
| Protein | ~3 grams |
| Carbohydrates | ~2 grams |
| Dietary Fiber | ~1.5 grams |
| Total Fat | ~0.4 grams |
| Saturated Fat | ~0 grams |
| Sodium | ~9 milligrams |
| Potassium | ~400 milligrams |
| Vitamin C | ~0.5 milligrams |
| Vitamin D | 0 micrograms |
| Calcium | ~3 milligrams |
| Iron | ~0.5 milligrams |
| Magnesium | ~14 milligrams |
| Phosphorus | ~91 milligrams |
| Zinc | ~0.5 milligrams |
| Copper | ~0.2 milligrams |
| Manganese | ~0.3 milligrams |
| Selenium | ~0.7 micrograms |
| Folate | ~8 micrograms |
| Niacin | ~2.5 milligrams |
| Pantothenic Acid (B5) | ~0.6 milligrams |
| Vitamin B6 | ~0.1 milligrams |
| Riboflavin (B2) | ~0.1 milligrams |
| Thiamine (B1) | ~0.1 milligrams |
Raw vs. Cooked Lion’s Mane
Raw Lion’s Mane mushrooms are commonly used fresh in salads and can be a rich addition to your diet. They maintain most of their nutrients in this state, but the texture and taste can be quite different from when they are cooked. Cooked Lion’s Mane has a flavor and texture akin to seafood, often compared to crab or lobster, making it a unique culinary delight. When cooked, the mushrooms become softer and may be easier to digest, which can be beneficial if you’re considering them for their potential health properties.
- Fresh mushrooms: Best when consumed soon after harvest for optimal nutrient retention.
- Dried Lion’s Mane: Can be rehydrated and used in cooking; nutrient density is more concentrated.
Nutrients and Vitamins in Lion’s Mane
Lion’s Mane is not just a gourmet’s choice but also a nutrient powerhouse. Your dietary intake from Lion’s Mane includes a spectrum of important vitamins and minerals.
- Vitamins: It contains vitamins such as the B-complex which are vital for neurological health and energy metabolism.
- Potassium: Crucial for maintaining heart function and regulating fluid balance.
- Phosphorus: Supports the formation of bones and teeth and is important in how your body uses carbohydrates and fats.
Nutrient Table:
| Nutrient | Benefit |
| B-Vitamins | Supports brain health and energy levels |
| Potassium | Regulates fluid balance and heart health |
| Phosphorus | Important for bone health and metabolism |
When incorporating Lion’s Mane into your diet, consider your overall nutrition and weight management goals. Whether you choose to eat it raw, cook it into a soup, or use it in powdered form, Lion’s Mane can be a versatile addition to a balanced diet.
Choosing Lion’s Mane Products
When selecting lion’s mane products for depression, focusing on quality and potency is essential for efficacy. This section will guide you through the considerations necessary to make an informed choice.
Quality and Purity Considerations
When considering lion’s mane supplements, look for products that specify the use of the fruiting body of the mushroom, as it’s the part that contains the highest concentration of bioactive compounds beneficial for health conditions such as anxiety, stress, and sleep disorders. Products should have clear labeling that indicates they have been tested for purity and are free from contaminants. Reputable brands often conduct third-party testing and can provide certificates of analysis.
To ensure quality, check if the supplement has been manufactured according to certified Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Additionally, opt for supplements that are organic certified, ensuring the lion’s mane was cultivated without harmful pesticides or herbicides.
Factors Affecting Potency
The potency of lion’s mane can vary greatly based on how the mushroom was grown, harvested, and processed. For addressing issues like depression, anxiety, and sleep quality, the dosage and extraction process of the supplement are critical.
- Extraction Method: Look for products that use a dual extraction process (water and alcohol) since some beneficial compounds are water-soluble, and others are alcohol-soluble.
- Standardization: Potency can also be guaranteed through standardization, where specific amounts of active compounds are present in each dose.
- Dosage: The product should provide dosage information that aligns with clinical research suggesting effective ranges for mental health benefits.
Be wary of products you might find at a grocery store that do not detail extraction methods or standardization as they may not provide the therapeutic benefits seen with high-quality medicinal mushroom supplements.
Frequently Asked Questions
When considering Lion’s Mane for depression, understanding the proper dosages and potential side effects is crucial for safe and effective use.
What is the recommended daily dosage of Lion’s Mane for depression relief?
The exact dosage of Lion’s Mane for depression has not been universally established due to varying product potency and lack of extensive research. However, doses in the range of 500-3000 mg per day have been referenced in various studies and anecdotal reports. It is advisable to start with a lower dose and monitor your response.
Are there any risks of taking too much Lion’s Mane?
While Lion’s Mane is generally well-tolerated, consuming it in very high doses may lead to discomfort such as gastrointestinal upset. It’s important to respect the recommended dosages and consult a healthcare provider if you plan on exceeding standard amounts.
Is it safe to include Lion’s Mane in my daily supplement regimen?
Lion’s Mane is considered safe for daily use when taken in recommended amounts. To ensure compatibility with your health condition and other supplements or medications, you should consult with a healthcare professional before adding it to your daily routine.
How does Lion’s Mane dosage vary when addressing neuropathy symptoms?
Research on Lion’s Mane for neuropathy is limited, and dosages may differ from those used for depression. Some studies suggest benefits at varying dosages, so it’s key to seek guidance from a healthcare provider before using Lion’s Mane for neuropathy to determine the appropriate amount for your situation.
What are the appropriate Lion’s Mane dosages for individuals with ADHD?
Dosage recommendations for Lion’s Mane in ADHD cases are not well-defined and can depend on individual factors. It is essential to talk with a healthcare provider to establish a safe and effective dosage tailored to the specific needs of someone with ADHD.
What side effects might be experienced when taking Lion’s Mane?
Most people do not experience adverse effects from taking Lion’s Mane in recommended doses, but some could encounter mild side effects such as digestive discomfort or allergic reactions. If you experience any side effects, it is best to consult a healthcare professional for advice.







